Artificial intelligence has evolved at an astonishing pace, and by 2025, AI is no longer limited to generating text or images. Two of the most talked-about technologies in the AI space today are Generative AI and Multimodal AI. While they may sound similar, understanding the difference between them is essential for businesses, developers, and enthusiasts who want to harness their full potential. In this article, we’ll dive into Generative AI vs Multimodal AI, explain how they work, explore real-world applications, and discuss why these technologies are shaping the future of AI-driven experiences.
What is Generative AI?
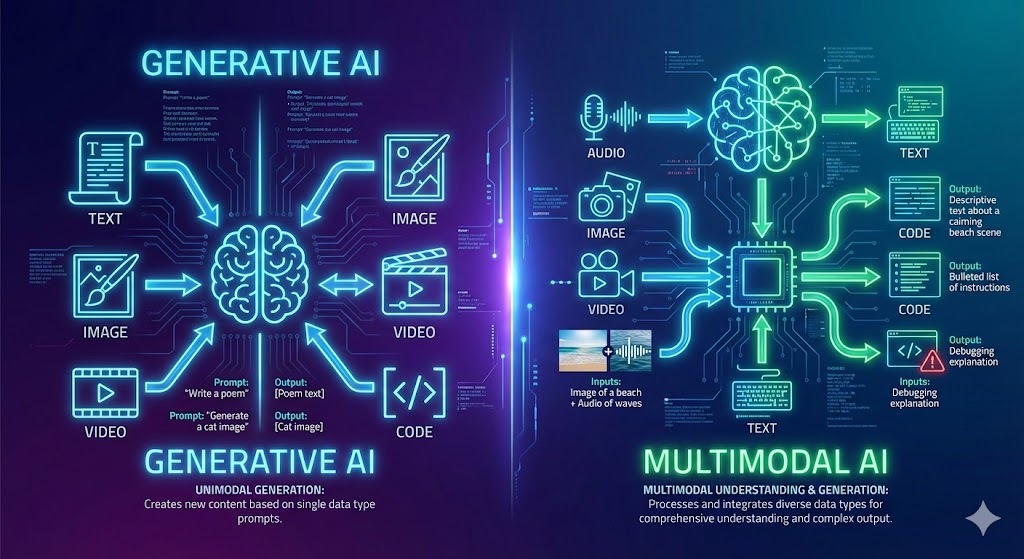
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems capable of creating new content. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on recognizing patterns or predicting outcomes, generative models are designed to produce original outputs in various formats. These can include:
How Generative AI Works
At its core, generative AI relies on large datasets to learn patterns and relationships in the data. Modern generative models, such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), use a process called transformer-based deep learning. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
-
Data Training: The model is trained on massive datasets, learning the probability of one word, pixel, or sound following another.
-
Pattern Recognition: The AI identifies structures, patterns, and context in the data.
-
Content Generation: Using learned patterns, the model generates new outputs that mimic human-like creation.
Examples of Generative AI
-
Chatbots generating human-like conversations
-
AI tools creating digital art from text prompts
-
Music composition AI generating new melodies
-
Code completion tools like GitHub Copilot
Generative AI is highly specialized in producing new content, usually from one type of input, such as text or an image. This is where it differs from multimodal AI.
What is Multimodal AI?
Multimodal AI, on the other hand, refers to models capable of processing and understanding multiple types of data simultaneously. These “modalities” include text, images, video, audio, code, and even sensor data. Multimodal AI is designed to integrate information across different formats, enabling more advanced reasoning and real-world problem-solving.
How Multimodal AI Works
Multimodal AI uses a unified representation system that allows it to map different types of data into a shared “embedding space.” This lets the AI understand relationships between modalities. Key steps include:
-
Input Processing: Accept multiple input types (text, images, video, audio).
-
Unified Representation: Convert inputs into embeddings that capture essential information.
-
Cross-Modal Reasoning: Interpret patterns and relationships across inputs.
-
Output Generation: Produce outputs in any format—text, structured data (JSON), images, code, or even video.
Examples of Multimodal AI
-
Upload a chart and text to interpret trends and generate a report
-
Provide an image of a product and receive a full e-commerce description
-
Upload a video clip to generate scene summaries and subtitles
-
Input hand-drawn wireframes to produce HTML/CSS code
Unlike generative AI, multimodal AI understands context across different types of information, making it far closer to human-like reasoning.
Generative AI vs Multimodal AI: Key Differences
Here’s a concise comparison to highlight the distinctions:
| Feature | Generative AI | Multimodal AI |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Usually single modality (text, image, audio) | Multiple modalities (text + image + video + audio + code) |
| Output | Single or specialized content type | Multiple content types (text, images, code, structured data) |
| Reasoning | Limited to one modality | Cross-modal reasoning across different data types |
| Examples | ChatGPT text responses, AI art generators | Google Gemini, AI that combines diagrams and text to generate code |
| Use Cases | Content creation, image generation, music, text summaries | Complex workflows, document processing, video analysis, multi-input problem solving |
Bottom line: All multimodal AI is generative, but not all generative AI is multimodal. Generative AI creates; multimodal AI understands, integrates, and creates across formats.
Real-World Applications of Generative AI vs Multimodal AI
Generative AI Applications
-
Content Creation: Blog posts, marketing copy, AI-generated books
-
Visual Arts: AI-generated illustrations, photo editing, and design
-
Audio & Music: Creating melodies, soundscapes, or voiceovers
-
Software Development: Code completion and suggestion tools
-
Entertainment: AI-generated scripts, gaming narratives, and animation
Multimodal AI Applications
-
Enterprise Productivity: Summarize documents, extract insights from charts, and generate reports
-
Video Analysis: Automatic scene description, subtitle generation, and object recognition
-
Creative Design: Convert sketches + text prompts into fully rendered graphics
-
Healthcare & Science: Analyze medical images, lab results, and textual notes simultaneously
-
Customer Support: AI that interprets screenshots, logs, and text queries for faster troubleshooting
Why Multimodal AI Matters in 2025
While generative AI has revolutionized content creation, multimodal AI pushes the boundaries further:
-
More Natural Interactions: Humans communicate using multiple modalities. Multimodal AI aligns with natural communication.
-
Advanced Reasoning: By combining inputs, the AI understands context better, leading to more accurate outputs.
-
Flexible Workflows: Developers and businesses can work across formats without switching tools.
-
Enterprise-Grade Solutions: Multimodal AI platforms like Google Gemini provide security, governance, and production-scale capabilities.
Google Gemini and Vertex AI: Leading the Multimodal Revolution
Google’s Gemini models, available via Vertex AI, represent the forefront of multimodal AI. These systems are designed to:
-
Accept text, image, code, and video inputs
-
Perform cross-modal reasoning to generate versatile outputs
-
Support enterprise security, governance, and large-scale deployment
Developers can experiment with Gemini using Google Cloud credits, opening up opportunities for AI-driven innovation across industries.
The Future of Generative AI vs Multimodal AI
By 2025, the distinction between generative AI and multimodal AI will shape how we interact with technology. Generative AI excels at producing specialized content, while multimodal AI enables deeper understanding and multi-step reasoning across different data types. Together, they are driving AI toward a more intelligent, human-like assistant, capable of seeing, reading, listening, understanding, and creating across multiple formats.
The impact spans industries: from healthcare and education to design, e-commerce, and entertainment. Businesses adopting multimodal AI early are likely to gain a competitive advantage, unlocking efficiency, creativity, and decision-making capabilities previously unattainable.
Conclusion
Generative AI vs Multimodal AI is more than a technical distinction—it reflects the evolution of AI itself. While generative AI revolutionizes content creation, multimodal AI brings us closer to truly intelligent, versatile AI systems capable of understanding and acting on the complexity of the real world.
In case you have found a mistake in the text, please send a message to the author by selecting the mistake and pressing Ctrl-Enter.
Sign In